Looking to maximize your trading profits? One of the key methods to control your trading costs is by understanding spreads. Yes, we are talking about the seemingly small differences between the bid and the offer prices. In this guide, we’re going to show you “what is a spread in forex trading”, and how it can influence the success of your trades.
We’ll also take you through how to choose the best broker with good and competitive spreads for your approach. Read on to discover what is a good spread in forex and why ParamountMarkets can be the best choice to help you trade wiser and more economically.
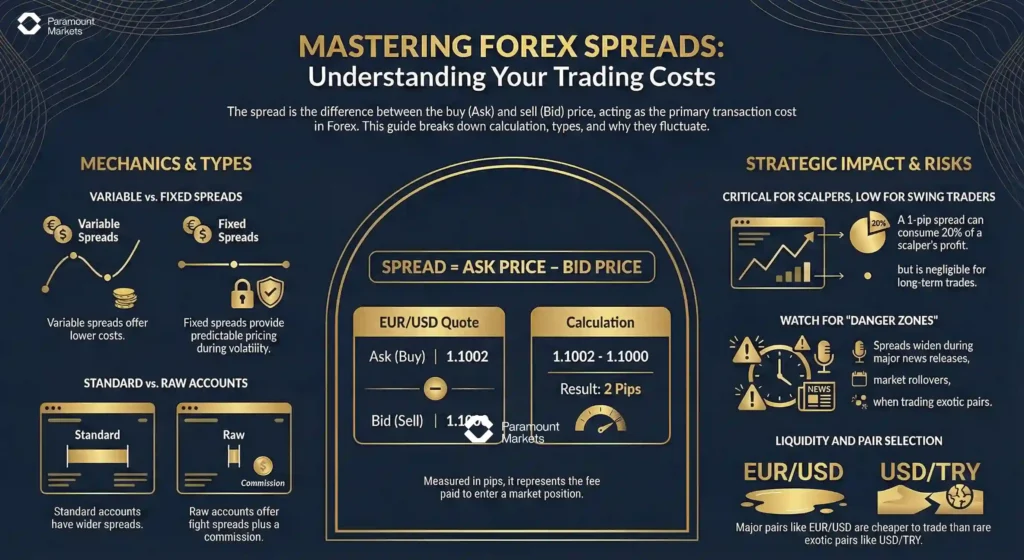
What is a Spread in Forex Trading?
In Forex trading, the spread is the tiny difference between the ask price (the price at which market participants are ready to sell) and the bid price (the price at which market participants are ready to buy) of a currency pair. Think of it as the hidden cost to establish a trade.
Example: EUR/USD is quoted at 1.1000/1.1002. In this example, the spread is 2 pips; 1.1002 (ask) minus 1.1000 (bid) = 2 pips.
Spreads are measured in pips, which are very small price movements (typically at the fourth decimal place). While they may seem insignificant, over time, these costs can really add up and eat into your profits. It is just like buying clothes; the shop buys them at a lower cost and sells them for a higher price.
How to calculate spread in forex
Forex spread calculation is simple and a basic ability that every trader should learn. Spread is simply the ask price (price at which you can buy a currency pair) minus the bid price (price at which you can sell the pair):
Spread = Ask Price – Bid Price
For example, if we use GBP/USD and the bid is 1.2500 with an ask of 1.2503. Subtract the bid from the ask:
1.2503 – 1.2500 = 0.0003 or 3 pips
Trading platforms like MT5 will display the ask and bid prices in real time. Also most brokers will even display the spread in plain sight.
So, knowing how to calculate spread in forex is good to know; but, you won’t have to calculate it yourself very often.
Forex Spread Cost Calculator
Calculating spreads manually is good practice, but in live trading, you need speed. Use our free calculator below to instantly convert the spread (in pips) into actual cash value (USD) based on your lot size. Knowing the exact cost helps you manage your risk before you even enter the trade.
Types of Spreads in Forex
Just as it’s important to understand what is a spread in Forex trading, it’s equally essential to get familiar with the types of spreads including fixed and variable (floating) spreads. In the following sections, we’ll break down each type along with their advantages and disadvantages, so you can choose what best suits your trading style.
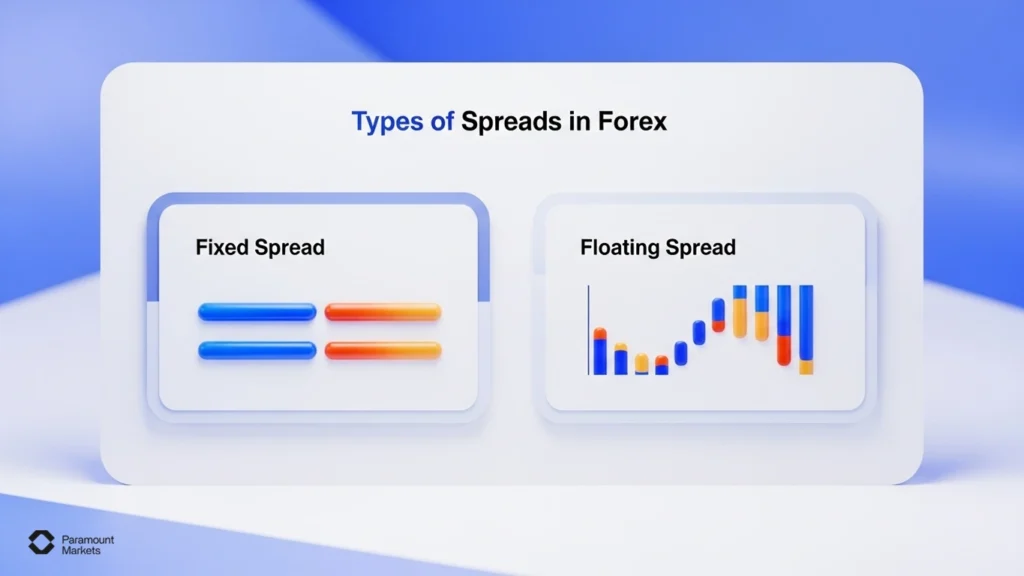
Fixed Spread
A fixed forex spread meaning that the ask and bid price difference stays the same, even when the market is volatile. This provides price certainty, which is very useful at news releases of economic data when variable accounts can experience their spreads widening.
- Predictability: Your costs will be the same regardless of market conditions.
- Beginner-friendly: The fixed spread forex account simplifies both trading activities and financial planning.
- Stable risk management: No surprise transaction costs during volatility.
- Higher cost in stable markets: Brokers charge you extra "insurance premium" for the stability.
- Less exposure to market conditions: Even when spreads should be low, you could still be paying higher fees.
- Reduced broker choice: Not every broker offers fixed-spread accounts (Requotes may occur).
Variable (Floating) Spread
A variable spread changes depending on market conditions. When there’s high liquidity (e.g., during the primary trading sessions), spreads tighten. But during times of volatility, like economic news events, they can widen significantly.
- Market-reflective: More accurate pricing based on prevailing market conditions (Supply & Demand).
- Lower average cost: In quiet markets (high liquidity), spreads can be near zero. Great for scalpers.
- Closer to interbank rates: Tends to be tighter and more competitive than fixed spreads.
- Unpredictable costs: Spreads can spike massively during major news or low-liquidity events.
- More complexity: Needs active monitoring; not "set and forget" like fixed spreads.
- Greater risk in volatility: Slippage can occur, and stop losses might trigger at worse prices.
The "Zero Spread" Trap
Don’t be fooled by “0.0 pips” advertising. Variable spreads are like a calm sea that can turn into a storm in seconds. Always check the average spread, not just the minimum, especially if you trade during news releases (NFP, CPI).
Comparison Table: fixed vs variable spread
Here’s a comparison of fixed and variable spreads based on essential trading factors to help you understand their practical differences.
| Feature | Fixed Spread | Variable Spread |
|---|---|---|
| Price Consistency | Always the same | Changes with market conditions |
| Cost Predictability | High | Low (can fluctuate) |
| Best For | Beginners, low-volatility strategies | Experienced traders, active hours |
| Spread Size | Slightly higher (includes risk buffer) | Can be lower, but varies |
| Market Reflection | Low | High |
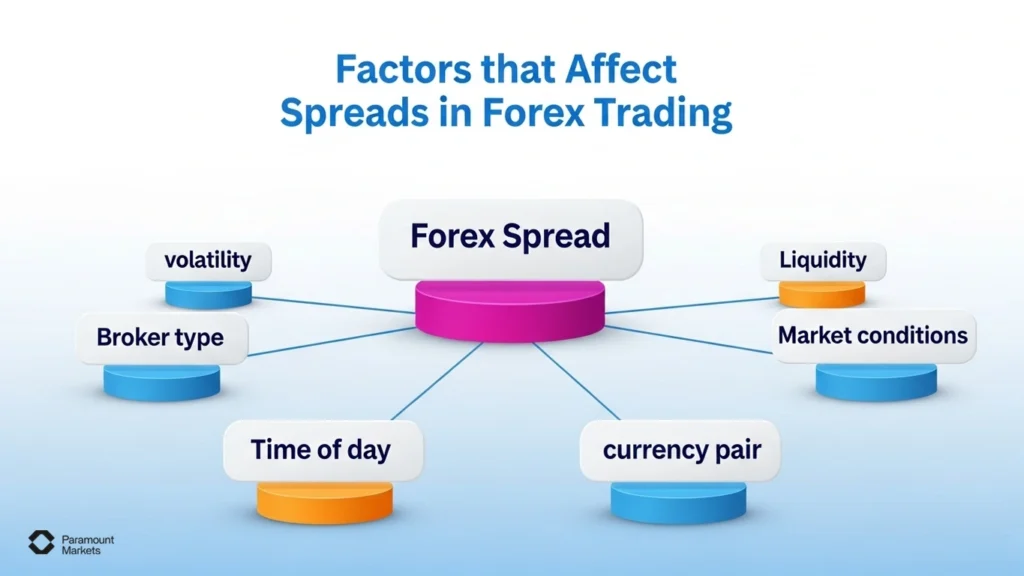
Factors that Affect Spreads in Forex Trading
Forex spreads are not constant and can vary due to several factors, including market volatility, liquidity, type of broker, time of day, and the specific currency pair being traded.. Spreads tend to widen during major news announcements when volatility and price fluctuations increase.
Currency pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD (known as major pairs) typically have tighter spreads due to higher liquidity, while exotic pairs (involving less commonly traded currencies) generally have wider spreads.
Spreads also narrow during busy sessions like the London-New York overlap and widen during quieter times.
Key Factors that impact spreads in forex trading includes:
Market Volatility
Spreads widen during major news and economic releases because of sudden price swings and increased risk.
For example, when the Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) data is released in the U.S., the spreads on USD pairs like EUR/USD can widen significantly in a matter of seconds, sometimes jumping from 1 pip to over 10 pips.
Liquidity
More trading activity usually leads to tighter spreads. For instance, major currency pairs have high liquidity, resulting in lower spreads. Exotic pairs, with less trading activity, have wider spreads.
For example: EUR/USD may have a spread as low as 0.1 to 1 pip during major trading hours due to its high liquidity, while an exotic pair such as USD/TRY might have a spread of 5–15 pips due to lower trading volume and market depth.
Broker Type
Market makers may offer fixed spreads or widen them during volatile market conditions. NND (No Dealing Desk) brokers provide variable spreads, which are closer to the actual market rates.
A typical example would be an NDD broker offering a spread of 0.2 pips on GBP/USD during the London session. A market maker that charges fixed spreads might set their spread at 2 pips for GBP/USD, regardless of the current market conditions.
Time of Day
Spreads are usually tighter during peak trading hours when market activity is high, and wider during off-peak hours.
For example, during the overlap of the London and New York trading sessions, when volume is high, a currency pair like USD/JPY may be traded with a 0.5 pip spread. The same currency pair may show a spread of 3 pips during the Asian session when the market is less active.
Currency Pair Type
Major currency pairs generally have the narrowest spreads, while minor and exotic pairs usually come with wider spreads.
For example, a minor pair like NZD/CHF could have a spread of 3–5 pips, and an exotic pair like USD/ZAR may have spreads exceeding 10 pips!
Market Conditions
News and market uncertainty combined with geopolitical surprises can lead to temporary widening of spreads in the financial markets. For instance, when unexpected economic news or geopolitical events occur, like an unforeseen central bank rate decision, spreads can widen across all major pairs.
How Spread Affects Your Trade
Spreads directly affect the cost, profit and choice of your trading strategies. This is why you must know what spread is in forex and its role in your trading activity.
Here are the main ways in which spread in forex can affect your trading decisions.

Trading Cost
A high spread means more transaction costs for trades. This is particularly important for active traders like scalpers who may open and close multiple trades in a day. The spread cost on each trade adds up quickly and eats into overall profitability.
Say the EUR/USD has a 3-pip spread. If you buy at 1.1203, your trade will immediately register a 3-pip loss because you can only sell it back for 1.1200. The price would have to move up to 1.1206 just for you to break-even.
Profitability
A wider spread also reduces the maximum profit you can take, especially on low-volatility markets with little price action. This limits your ability to realize profits after accounting for spread costs.
Strategy Choice
Scalping and day trading require tight spreads to be able to continue earning money as they depend on small, quick price movements. Swing traders, holding positions longer and seeking larger moves, are less concerned with the size of the spread. In brief, tighter spreads most benefit scalpers and day traders.
Say the EUR/USD has a 3-pip spread. If you buy at 1.1203, your trade will immediately register a 3-pip loss because you can only sell it back for 1.1200. The price would have to move up to 1.1206 just for you to break-even.
Spread vs Commission in Forex, What’s the Difference?
For Forex trading, two common methods that brokers will charge fees are commissions and spreads. The spread refers to the price difference between buying and selling, often incorporated into the trade price.
Some brokers charge a separate fee called a commission on each trade. Others don’t charge a commission but make money by offering wider spreads instead. This means you’re paying either way through a visible fee or a hidden cost in the price difference.
Key differences between spread vs commission forex are discussed in the following table:
| Aspect | Spread | Commission |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Structure | Built into the price of the trade | Charged separately per trade |
| Impact on Trading Style | More significant for frequent, small trades like scalping | More relevant for large volume or long-term trades |
| Predictability | Variable; can fluctuate with market conditions | Usually fixed or clearly stated |
| Transparency | Less obvious, as cost is embedded in the trade price | More transparent, clearly itemized |
| Effect on Profitability | Can add up quickly with many trades if spreads are wide | Easier to calculate but adds fixed cost |
| Typical Broker Approach | Some brokers widen spreads to avoid commissions (Standard Accounts) | Brokers charge commissions with tighter spreads (ECN/Raw Accounts) |
ParamountMarkets stands out for providing tight spreads and no commission on most accounts. This means transparent pricing with no hidden fees. This is beneficial for traders, particularly active ones, in keeping costs low and consistent with no surprises.
How to Choose a Broker with Good Spreads
When trading Forex, your broker can have a substantial impact on your bottom line, especially in the form of the spreads they offer. Using a broker with tight spreads means you get to keep more of your profits and avoid surprise.
Here’s what traders should look for:

Transparency in Spread Pricing
You want a broker that clearly shows their spread fees without hidden fees. You can better manage your trades when you understand precisely what you’re being charged.
Secure Trading Platforms
A smooth, stable platform like MetaTrader 5 (MT5) is not only convenient, but it can also play a big role in how well you’re doing in entering and leaving trades at optimal times, avoiding slippage and fees.
Major Pair Competitive Spreads
Look for brokers offering spreads below 1 pip for high-liquidity currency pairs like EUR/USD. Tighter spreads save you money, especially if you’re a frequent trader.
Note: Paramount Markets offers spreads of less than one pip on EUR/USD, helping you keep trading costs low.
Account Options
Brokers offer more than one account; such as standard accounts with regular spreads and pro accounts with tighter spreads but larger minimum balances. Choose one appropriate to your trading strategy and your funds.
ParamountMarkets’ Spread Offering
ParamountMarkets understands that low spreads are critical for trading success. That’s why we offer some of the best spreads in the market, including on the major pairs such as EUR/USD. We are also transparent with our pricing. There are no hidden fees or commissions.
Whether you’re a scalper needing ultra-low costs or a long-term trader seeking reliability, Paramount Markets delivers.
Here are some reasons why traders pick ParamountMarkets:
- Spreads from 0.0 pips (pro account): Extremely low forex trading costs to maximize your profit potential.
- Swap-free accounts available: Ideal for traders who require Islamic-compliant trading options.
- No hidden fees or commissions: Transparent pricing with no surprises to affect your bottom line.
- Local payment methods & 24/7 support: Cryptocurrencies and tether deposits and withdrawals plus round-the-clock assistance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Spreads
Spreads in Forex trading can seem like no big deal, but forgetting how they work will end up costing you big.
The following section highlights typical mistakes in spread management along with strategies to prevent financial losses and mental strain for investors.
- Trading high-spread pairs blindly without understanding the cost can eat away at your profits fast, particularly with exotic currencies that inherently have higher spreads. Be sure to check average spreads before trading new pairs.
- Forgetting spread widening during periods of uncertainty, such as major news announcements, can yield higher cost or unforeseen losses as spreads have a tendency to increase when there is decreasing liquidity. Understanding economic calendars and avoiding trading during such periods will help reduce these risks.
- Selecting a low spread forex broker can be dangerous because low spreads do not always translate to good service. Brokers who advertise low spreads may experience issues with execution, hidden commissions, or poor customer support. Spread costs need to be weighed against the broker’s reliability and overall quality.
Avoiding these mistakes not only protects your capital but also makes for a smoother, more confident trading experience. An understanding of spreads in detail and trading sensibly around them is crucial to long-term success.
Conclusion
Spreads play a crucial role in your fees and gains. Having a broker that offers tight spreads can make a real difference. After ParamountMarkets offers competitive spreads of just 0.0 pips in pro account, no extra fees, and no commissions; offering low-cost trading conditions.
This makes ParamountMarkets an ideal option for traders who like to keep things cheap and focus on their strategy without worry.
FAQ
What is considered a good forex spread?
For major pairs like EUR/USD, a spread under 1.0 pip on a Standard account is considered competitive. On Pro or Raw accounts, spreads should be near 0.0 pips, though these usually come with a separate commission fee.
Are lower forex spreads always better?
Not necessarily. Extremely low spreads often come with commissions or hidden costs. Also, a broker might advertise 0.0 spreads but have poor execution speed (slippage). Always look at the total trading cost (Spread + Commission), not just the spread.
Do spreads change during the day?
Yes. Spreads are tightest during the London-New York overlap (peak liquidity). However, they tend to widen significantly during the daily rollover (market close) and off-hours like the early Asian session due to low liquidity.
Why do forex spreads widen during news events?
During high-impact news (like NFP or CPI), liquidity providers pull their orders to protect themselves from volatility. This lack of liquidity forces brokers to widen spreads to cover the increased risk of executing trades at unstable prices.
Which is better: Fixed or Variable Spread?
Variable spreads are generally cheaper and better for most traders, as they reflect true market prices. Fixed spreads are mostly useful for beginners or news traders who want to avoid surprise cost spikes during volatility.
Does spread affect my stop loss?
Yes, absolutely. Since the Ask price (used to close Sell orders) is higher than the Bid price, a widened spread can hit your Stop Loss even if the chart price didn’t seem to touch it. Always account for the spread when placing your SL.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice, investment recommendations, or an offer to buy or sell any financial instruments. Trading Foreign Exchange (Forex) and Contracts for Difference (CFDs) involves a high level of risk and may not be suitable for all investors. Leverage can work against you as well as for you. Before deciding to trade, you should carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, and risk appetite. You should not invest money that you cannot afford to lose.
