Many traders jump into the forex market with high leverage, hoping for big profits. But their poor risk management becomes a huge trouble along the way. Leverage can be your best friend or your worst enemy. If you do not understand it fully you will lose money quickly.
Forex leverage allows you to control a much larger position with relatively little capital. So, traders can potentially amplify returns; but also increase risks. That’s why understanding leverage in forex is crucial and you need to understand how leverage works if you’re looking for long-term success.
In this ParamountMarkets blog, we’ll break down what is forex leverage, how it works, and real examples to help you use it wisely.
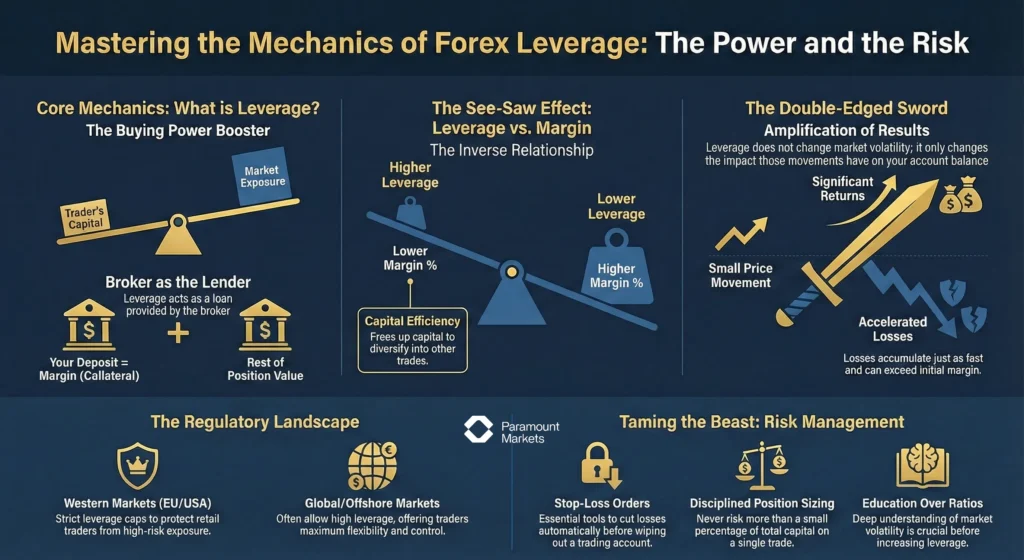
What is forex leverage?
Leverage in forex trading allows you to control a large position with a relatively small initial investment, known as margin. It essentially functions as a broker-provided loan that enables you to trade larger positions than your available capital would normally permit.
This way you can take advantage of small price movements in the forex market, which might not be profitable otherwise with a limited investment. The diagram below shows how using leverage can reduce the capital requirement for the same profit.
How does leverage work? The Mechanics of Leverage
To understand how leverage works in forex, let’s first think of it as a financial boost that lets you trade larger positions than your actual capital.
When you use leverage, the broker provides a portion of the trade’s value, requiring only a small margin from you. This means you’re not fully funding the trade yourself; instead, the broker lends you the remaining.
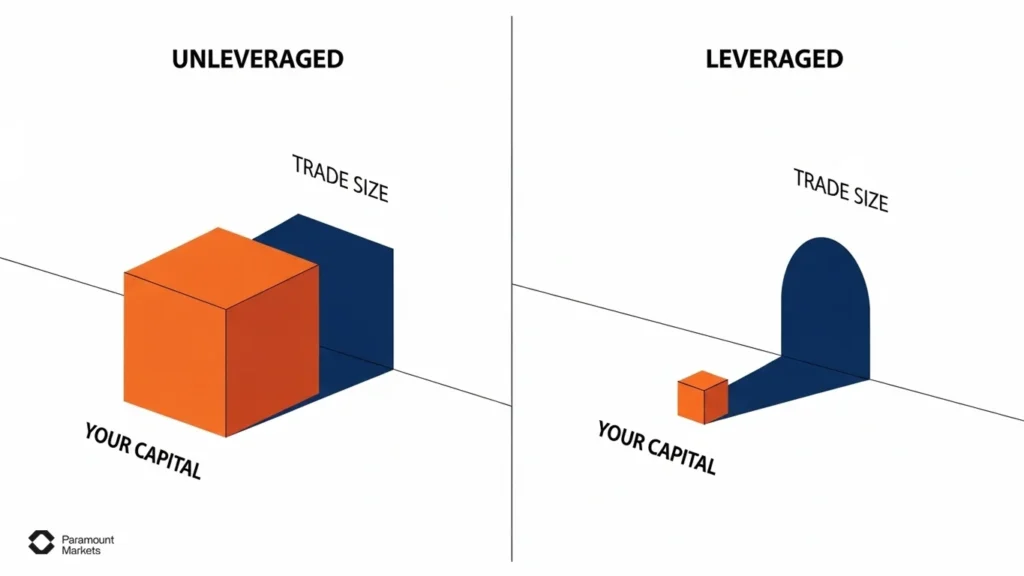
Example of How Leverage Works
Let’s break down forex leverage examples with a simple scenario. Consider the following situation:
- You have $1,000 in your trading account.
- Your broker offers a 1:100 leverage ratio in forex trading.
- This means you can control a position worth $100,000.
Now, assume you decide to trade EUR/USD at an exchange rate of 1.1000:
- You buy 1 standard lot (100,000 units) of EUR/USD at 1.1000. In this case, each pip is worth $10.
- If the price rises from 1.1000 to 1.1050 (50 pips increase), your position’s value increases by $500 (50 × $10). With your initial $1,000 investment, this means a 50% profit.
In simple terms, leverage lets you trade with more money than you actually have. With 1:100 leverage, your $1,000 acts like $100,000, and this allows you to make bigger trades. In this example, a small price increase gave you a $500 profit, which is 50% of your initial investment. This shows how leverage can boost your earnings.
However, if the market goes against you and price drops by 50 pips instead, your position’s value decreases by $500, which means you’ve lost half your capital in just a single trade!
How to Calculate Leverage in Trading
Are you confused about how to calculate leverage in trading? You are not alone.
Leverage is a concept that seems to be used differently by different people. Yet, knowing the math behind it and how to apply it to your trade setup is extremely important for proper risk management and trade planning.
In fact, leverage calculations are very simple math, and in this guide, we will make sure you learn how to calculate leverage for any trading scenario.

Leverage Calculation Formula
The basic formula to calculate leverage is:
- Total Position Size is the full value of the trade you’re opening.
- Equity refers to the amount of money you’re using from your account (your margin).
Example:
Let’s say you want to trade a position worth $50,000, and you’re using $1,000 from your account as margin. Your leverage would be:
Leverage = 50,000 / 1,000 = 50
This means you’re using 1:50 leverage – for every $1 you contribute, your broker allows you to control $50 in the market.
Forex Leverage Calculator
If you’re unsure about the numbers, using a Forex leverage calculator can save time and reduce mistakes. Many brokers offer free tools that automatically compute your leverage based on the trade size, margin, and leverage ratio.
To make this even easier, you don’t need to do the manual math every time. Use our free Forex Leverage Calculator below to instantly check your numbers, find your required margin, and plan your trades with precision:
Why It Matters
Knowing how to calculate leverage helps you:
- Understand your true market exposure
- Assess risk-to-reward ratios accurately
- Avoid overleveraging, which can lead to larger losses
What is Margin and How Does it Relate to Leverage?
Margin in forex trading refers to the amount of money required to open and maintain a leveraged position. You can’t access this money until your position is closed. In simple words, leverage boosts your buying power, while margin is the minimum amount you must maintain as collateral.
Margin and leverage calculation formulas are:
For example, you can open a position that is 100 times the size of your deposit. This is leverage of 1: 100 with a margin requirement of only 1%. Managing your margin properly, ensures that you have enough funds in your account to cover potential losses and avoid a catastrophe, margin calls.
What Is a Leverage Ratio?
The leverage ratio for forex trading determines your permitted leverage amount through a ratio format such as 1:50 or 1:100. This ratio shows how much larger a position you can control with your margin.
As an example, a leverage ratio of 1:100 means you can control $100 in the market for every $1 of your deposit.
The following chart shows how varying levels of leverage influence your exposure:
| Leverage Ratio | Investment | Exposure (Buying Power) |
|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | $1,000 | $1,000 |
| 1:20 | $1,000 | $20,000 |
| 1:50 | $1,000 | $50,000 |
As you can see, forex margin and leverage work together. It is important to keep in mind that leverage magnifies the potential for both profit and loss.
Note: Leverage is also available for currency pairs. This can vary for several reasons including broker rules, volatility, etc. For example, if you were to trade on 5% margin, you would only need to put up $500 to control $10,000 worth of USD/CHF.
Forex Leverage: Your Friend or Your Enemy?
Forex leverage can magnify your losses just as easily as your gains. If the market moves significantly in the wrong direction, you may face a margin call. It requires you to deposit additional funds to keep your position open or risk having it closed automatically. So, it’s a good idea to understand the pros and cons of leverage before using it.

The Benefits of Using Leverage in Forex
If you use the advantages of leverage wisely, you can maximize your profit potential and improve capital efficiency.
- Magnified Profits: Through leveraged trading you can manage a larger position with minimal upfront capital. This means that even small price movements can lead to large profits.
- Gearing Opportunities: Leverage can also free up capital for you to invest in other opportunities, allowing you to diversify your portfolio.
- Capital efficiency: Leverage lets you use your available capital to back several trades simultaneously. For example, with limited funds, you can enter various currency markets simultaneously, diversifying your risk and potentially increasing your overall profit.
The Risks of Using Too Much Forex Leverage
We know that leverage can provide significant rewards, but it also brings significant risks, especially when used recklessly or without a proper understanding of risk management. Risks of Using Too Much Leverage includes:
- Magnified Losses: On the flip side, if the market moves against you even slightly, your losses can quickly exceed your initial margin.
- Margin Calls: If your position moves in the opposite direction and your margin falls below a certain level, your broker may issue a margin call. This requires you to deposit more funds into your account to keep the position open, or you’ll be forced to close it, potentially locking in a loss.
- Increased Emotional Stress: Trading with high leverage can lead to emotional strain.
- Overtrading: The temptation to overtrade with leverage can be strong. It’s important to resist this urge and trade responsibly.
How Much Leverage Should I Use?
The amount of leverage you use should align with your:
- risk tolerance
- experience level
- trading strategy
New forex traders should choose lower ratios such as 1:5 or 1:10. This will allow for some risk management while getting accustomed to the market. The medium experienced forex traders, those that know the working of leverage in forex trading, may take on higher ratios of 1:50 or 1:100.
Important Tips for Using Leverage
The secret to leverage is combining smart risk management with disciplined execution. Here are a few critical tips to help you use leverage safely while maximizing your profits.

Watch Your Leverage Ratios and Margin Calls
Using a lower leverage ratio in forex trading reduces the impact of market volatility on your capital. This way, you will have more room to weather the storm when prices move unexpectedly without wiping out your account.
Remember that if your margin level gets too low, you may receive a margin call or liquidation. Keeping an eye on your forex margin and leverage helps prevent unexpected account depletion. Always ensure you have enough free margin before opening new positions.
Limit Your Position Size
A good rule of thumb is to never risk more than 1-2% of your total capital on a single trade. By following this principle you maintain enough resources to continue trading even after a bad trade. To further strengthen your risk management strategy, use a forex leverage calculator to determine the best position size based on your risk tolerance and trading capital efficiency.
Always Set Stop-Loss Orders
Trading with leverage creates market volatility which makes protecting your capital essential. Stop-loss orders are a must when you trade with leverage in the forex market. It is an order that automatically closes your position if the market price reaches a predetermined level. This helps you manage potential losses.
Practice with Demo Accounts and Educate Yourself
Since leverage can amplify both gains and losses, it’s crucial to manage your risks.Before using high forex trading leverage, take time to learn market behavior and develop a solid trading strategy. Diversifying across multiple assets reduces the impact of any single losing trade on your overall capital.
Also, practicing with a demo account allows you to test different forex leverage examples without risking real money.
Leverage Regulations in MENA and Global Markets
Leverage regulations in the forex market can differ significantly depending on the region, with some markets having more stringent rules in place to protect traders from taking on too much risk.
In some cases, leverage can vary from one jurisdiction to another within a region.
For instance, in MENA, every country follows its unique set of rules:
In the UAE, where forex brokers are regulated by the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) and the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), retail forex leverage is often capped at 1:50 or lower.
Meanwhile, Saudi Arabia’s Capital Market Authority (CMA) recently has introduced stricter controls on retail trading, limiting participation and imposing strong risk-mitigation requirements.
ParamountMarkets, Exness and XM are among the increasing number of brokers that offer swap-free Islamic accounts with margin trading capabilities.
Globally, leverage regulations are more established:
In most cases, major central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (Fed) of the U.S., the European Central Bank (ECB) of the Eurozone, and the Central Bank of the UAE (CBUAE), do not directly set leverage limits. Those are set by regulators (CFTC/NFA, ESMA, SCA/DFSA, etc.).
In general, leverage rules are stricter in Europe and the U.S. For instance, the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) caps forex leverage at 1: 30 for majors currencies and 1:20 for minors, while the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and National Futures Association (NFA) have a much stricter of 1:50 for major pairs and 1:20 for minors.
In Australia, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) also enforces the 1:30 limit, similar to ESMA.
However, in international and offshore markets, regulatory frameworks are designed to offer greater trading flexibility. Brokers in these regions can provide much higher leverage, often up to 1:500.
Instead of imposing strict restrictions like in Western markets, these jurisdictions cater to experienced traders who require higher buying power and have the discipline to manage their own risk.
It creates an environment where you have full control over your margin strategy, rather than being limited by tight regulatory caps.
Start Trading Forex in Paramount Markets
If you want to take advantage of forex leverage in a secure and efficient trading platform which is compatible with (Metatrader versions), ParamountMarkets is the perfect place to start.
You can manage your risk and control your trades with forex leverage up to 1:500. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, our brokerage offers competitive spreads, reliable execution, and top-tier customer support to help you succeed.
Sign up now and start your financial activities in ParamountMarkets.
Forex Leverage FAQ
What forex leverage is good for $100?
For a small account like $100, leverage between 1:100 to 1:200 is practical. It allows you to open micro-lots (0.01) with sufficient free margin. While higher leverage like 1:500 is available, it requires strict discipline, as a small market move can quickly deplete a small balance.
What does 1:500 leverage mean in forex?
A 1:500 leverage ratio means you can control $500 in the market for every $1 of your own capital. For example, a $100 deposit lets you control a position worth $50,000. While this maximizes potential returns, it also amplifies losses just as fast.
What is a good leverage in forex?
There is no ‘best’ leverage, only what fits your strategy. Beginners should typically start with lower ratios like 1:30 or 1:50 to limit risk exposure. Experienced traders often use 1:100 or higher to execute scalping strategies or manage multiple positions simultaneously.
Can leverage make me lose more money than I deposited?
It depends on your broker. At ParamountMarkets, we offer Negative Balance Protection, ensuring that you never lose more than your initial deposit, even if the market moves drastically against a highly leveraged position.
Does higher leverage change the value of a pip?
No, leverage does not change the pip value; it only changes the amount of margin required to open the trade. Pip value is determined by your lot size (volume), not your leverage ratio.
Is higher leverage better for beginners?
Generally, no. While higher leverage requires less margin to enter a trade, it leaves less room for error. For beginners, lower leverage acts as a safety net, preventing you from opening positions that are too large for your account size.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice, investment recommendations, or an offer to buy or sell any financial instruments. Trading Foreign Exchange (Forex) and Contracts for Difference (CFDs) involves a high level of risk and may not be suitable for all investors. Leverage can work against you as well as for you. Before deciding to trade, you should carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, and risk appetite. You should not invest money that you cannot afford to lose.
